Blog
Multiple Sclerosis
Facts about MS.
- Canada has the largest number of individuals with MS in the world. 1 in 340 Canadians are living with MS.
- MS symptoms occur in episodes that occur months or years apart and affect different anatomic locations in the body.
- Diagnosed between the ages of 20 to 49
- MS is three times as likely to occur in women as in men
- Common in people of northern European background.
What is Multiple sclerosis?
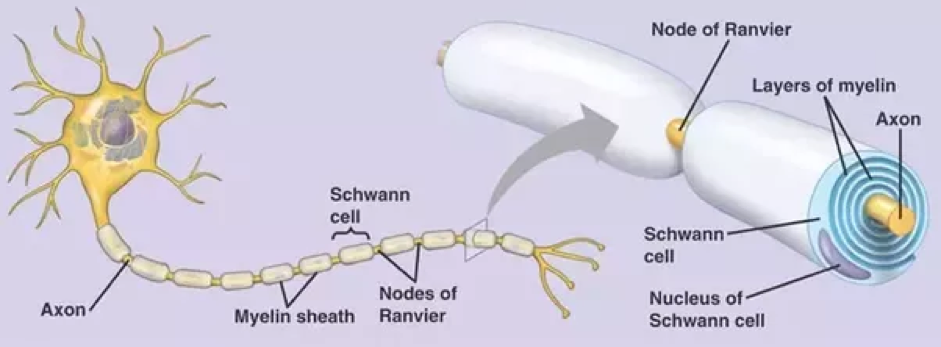
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease. An autoimmune disease is in which the body attacks itself. In MS, the body produces antibodies which attack the myelin sheath of the nerve cells in the Central Nervous System (brain and spinal cord). Myelin sheath is the protective layer surrounding the nerve cells. Myelin protects the nerve cells and helps transmit signals across the nerve. If myelin is damaged and is replaced by scar tissue, this leads to loss of signal transmission across the nerve cell.
Recognize the signs and symptoms
- Fatigue
- Dizziness
- Vision problems
- Numbness/tingling
- Problems with balance
- Tremor
- Hyperreflexia
- Spasticity
- Depression
- Bladder, Bowel, and Sexual dysfunction
- Heat intolerence
- Pain
What causes MS?
After decades of research, the cause of MS is still a mystery. However, one thing is for certain that lifestyle, genetics, and biological factors all play a role in the development of MS.
Classification of MS
- Relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS): Approximately 85% of cases
- Secondary progressive MS (SPMS)
- Primary progressive MS (PPMS)
- Progressive-relapsing MS (PRMS)
Detection
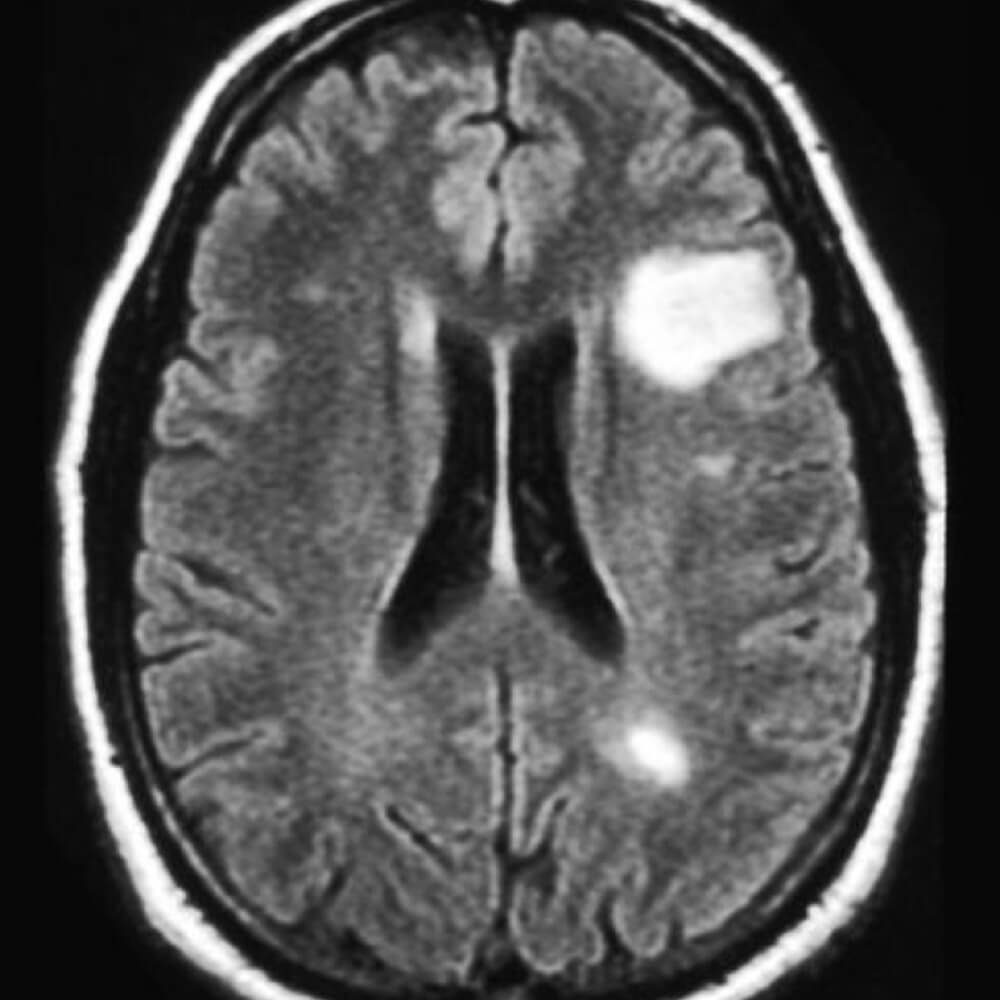
- The test of choice is MRI.
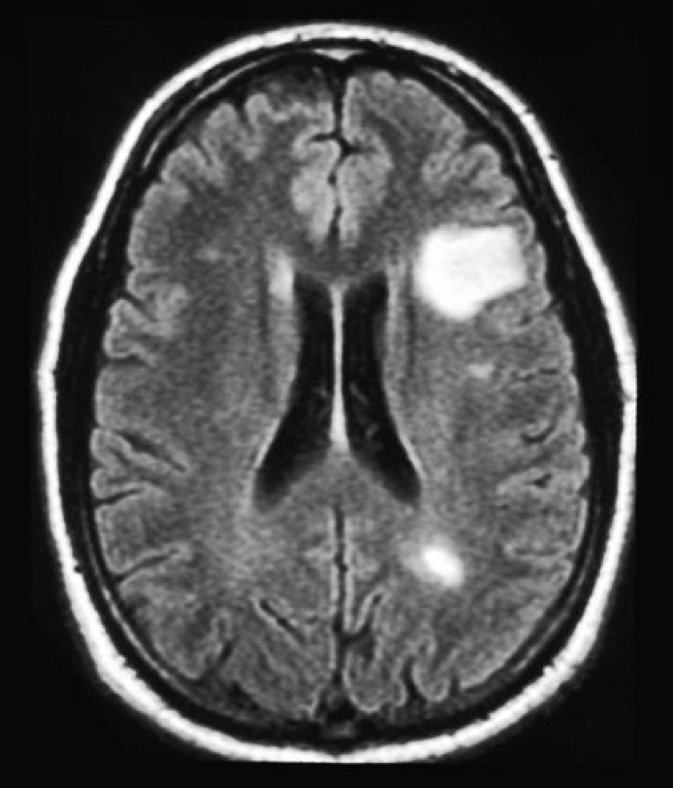
- Lumbar puncture (LP) – If MRI is not diagnostic. During a LP, small amount of CSF fluid is aspirated via the back through the spinal column and is lab tested for MS.
Treatment
There is currently no cure for the disease. However, there are various treatment options that are available that have been proven to be beneficial.
During an acute exacerbation
Methylprednisolone
Plasmapheresis (Plasma Exchange)
Dexamethasone
Drugs that prevent relapse and progression
Interferon Beta – 1a
Interferon Beta – 1b
Peginterferon Beta – 1a
Glatiramer acetate
Natalizumab
Fingolimod – first oral drug for MS
Mitoxantrone
Daclizumab
Alemtuzumab
Dalfampridine
Teriflunomide
Azathioprine
Cyclophosphamide
Symptom specific Treatment
Fatigue – Amantadine, Methylphenidate
Spasticity – Baclofen, Tizanidine.
Depression – SSRIs
Pain – Tricyclic antidepressants
For More information
Visit Multiple Sclerosis Society of Canada at www.mssociety.ca
You can also visit one of our locations and speak to one of our doctors if you have any questions or concerns. Please visit our website at www.nationalmedicalgroup.ca.
